.jpg)
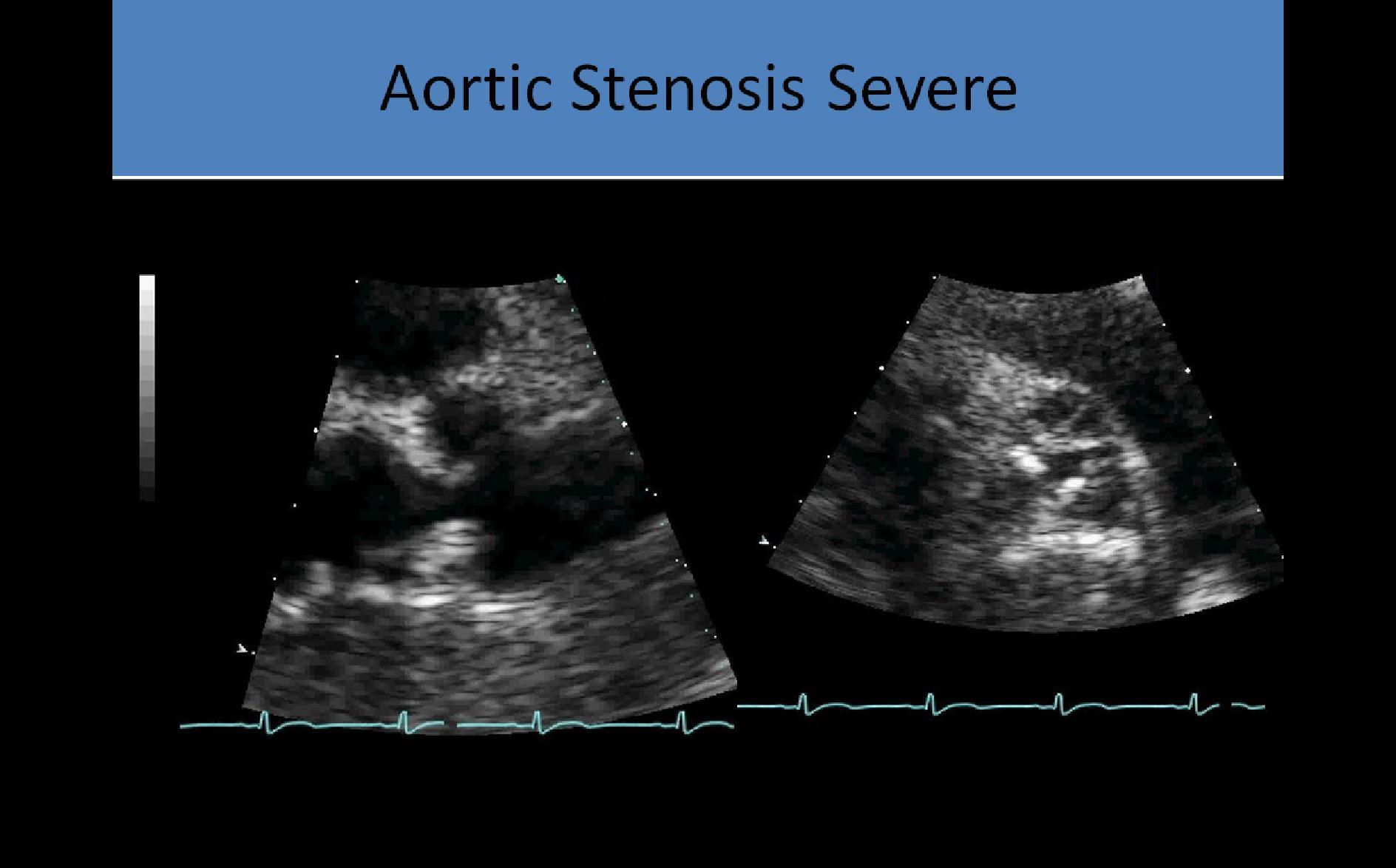
Aortic Valve Stenosis
Primary vs. Secondary Findings:
- A primary finding refers to the primary cause of the abnormality
- EX: atherosclerosis formation on the aortic valve causes the stenosis
- A secondary finding refers to other abnormalities caused by the primary abnormality
- EX: aortic stenosis causes thickening of the LV wall and post-stenotic dilatation of the aortic root
Considerations When Evaluating Cardiac Valves:
- How many valve leaflets are present?
- Do you see abnormal masses, thickening or calcification attached to the valve leaflets?
- Is leaflet mobility normal, restricted or hypermobile?
- What are the associated abnormalities of the cardiac chambers and other cardiac valves?
Aortic Stenosis - Atherosclerosis:
- Most common primary heart valve disease
- Echocardiography is the preferred noninvasive imaging method for evaluation of suspected AS
- Degenerative disease is the most common cause of aortic stenosis
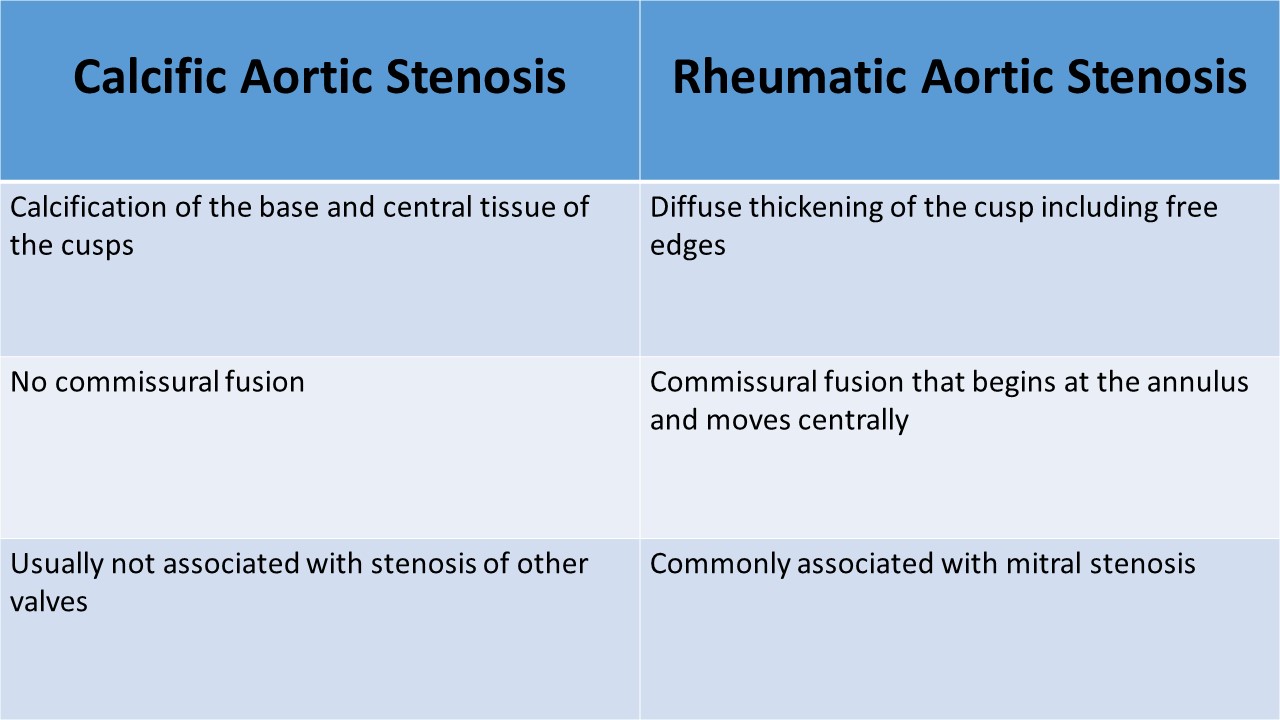
- Degenerative changes of a tri-leaflet valve begin at the sinus and spread toward the center of the valve, without commissural fusion
- Calcification of a bicuspid valve is often more asymmetric
- Rheumatic AS is characterized by commissural fusion and raphe formation; it is usually accompanied by rheumatic MS
- Systemic inflammatory diseases like ankylosing spondylitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, cause leaflet thickening and aortic aneurysm formation
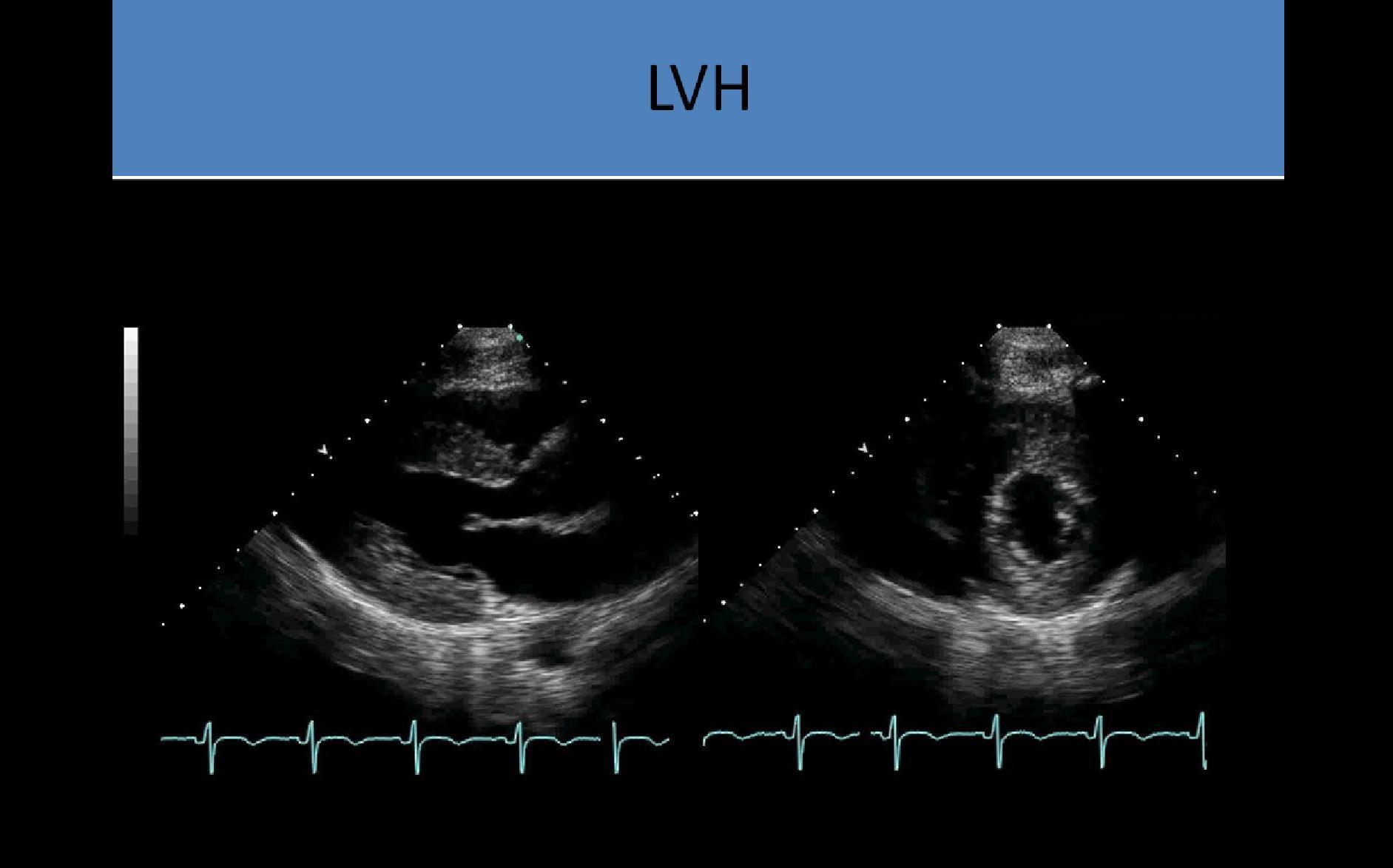
- Hypertrophy of the muscle wall of the ventricle will occur as it adapts to the chronic pressure overload
Clinical Symptoms:
- Dyspnea/Shortness of breath most common symptom
- Orthopnea
- Palpitations
- Fatigue
- Dizziness and syncope due to decreased cardiac output
- Harsh systolic crescendo-decrescendo murmur best heard at the right upper sternal border
- Systolic ejection click
- Significant stenosis can lead to angina due to reduced cardiac output to the aorta and coronary arteries
- Significant stenosis can lead to a cerebral infarct/ischemia caused by reduced cardiac output
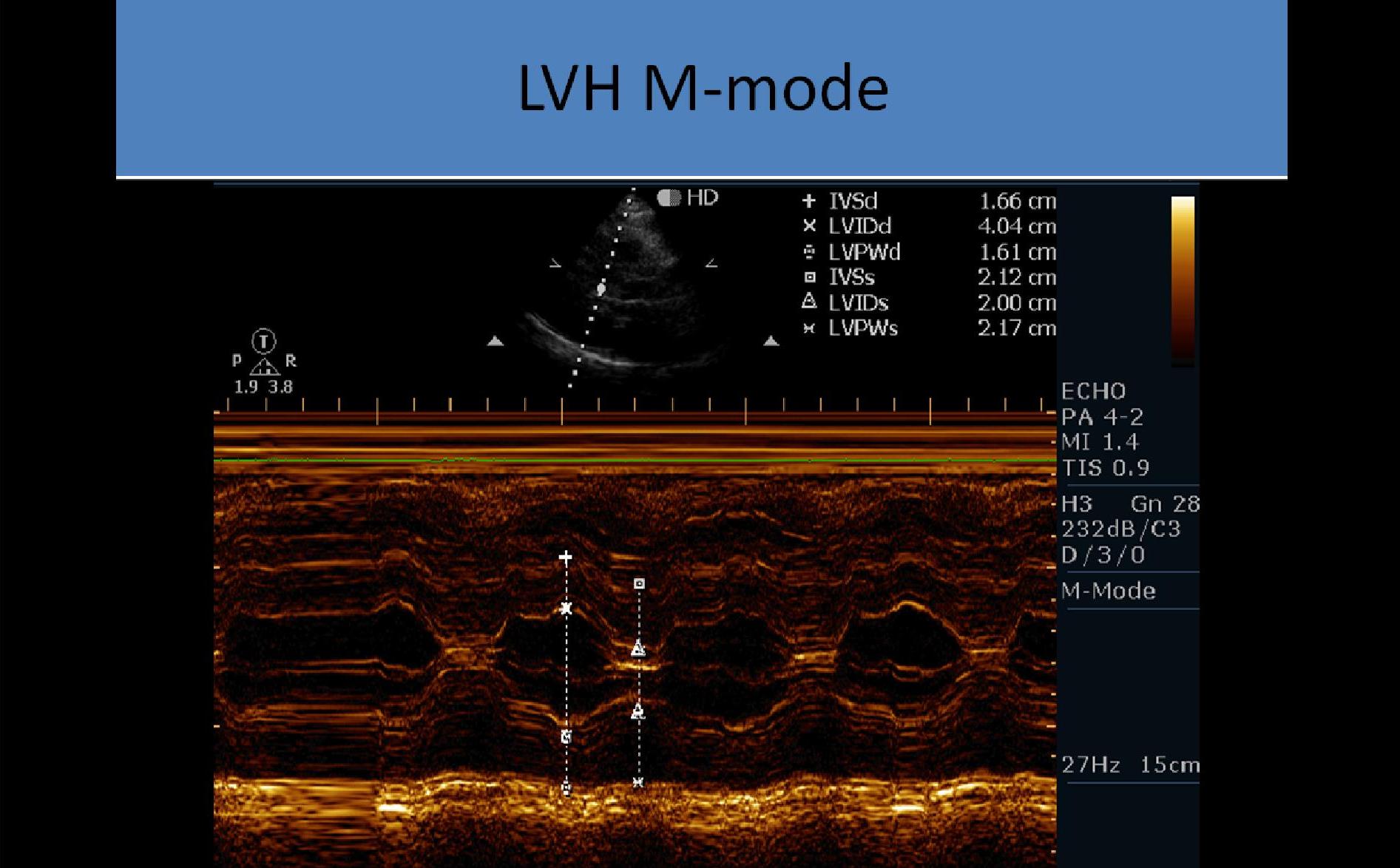
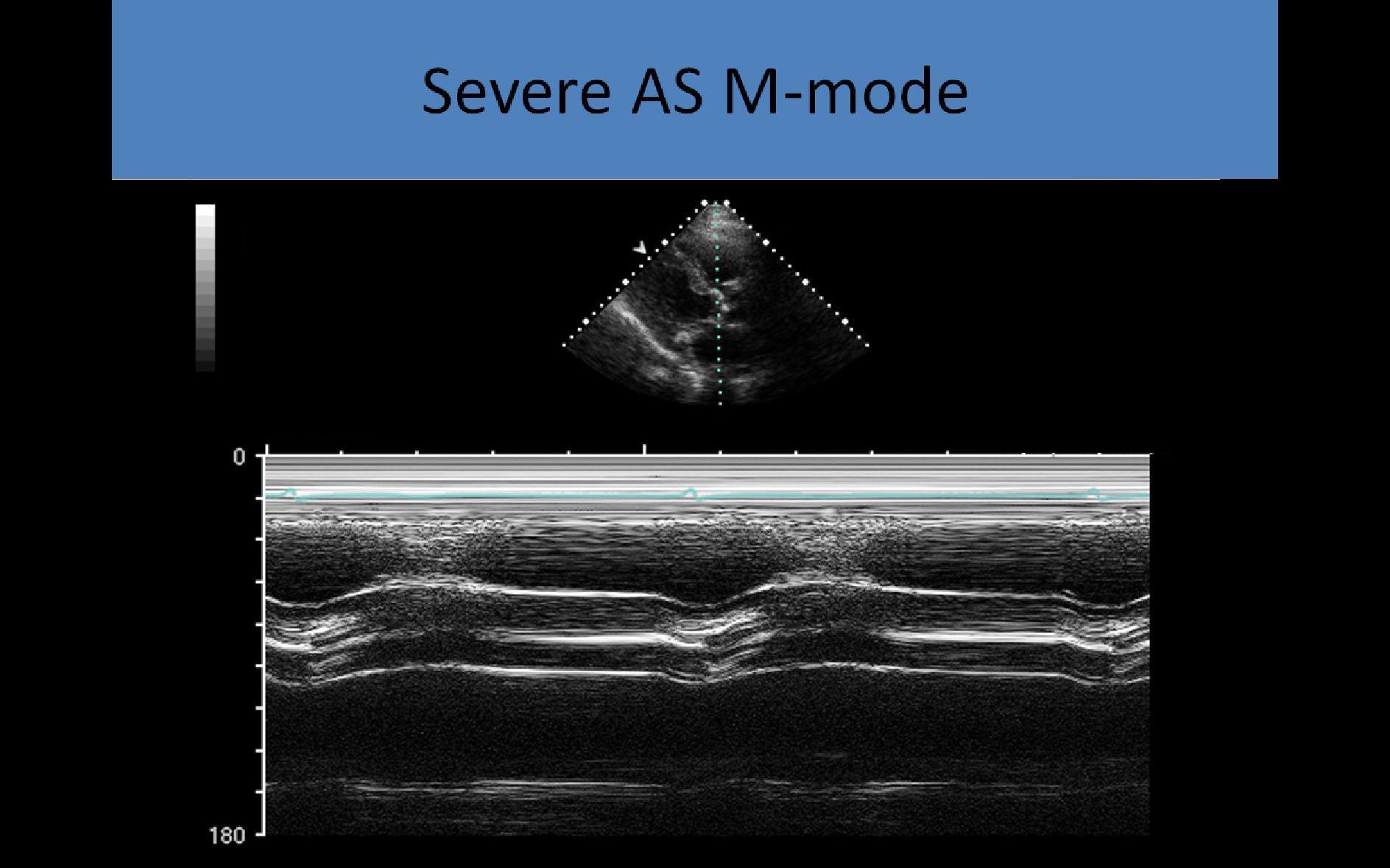
M-mode:
- Used to assess systolic leaflet separation
- <12 mm cusp separation indicates significant obstruction
- Method is not very accurate in determining the severity of the stenosis
- Thickened leaflets cause multiple echoes to be displayed in diastole
- Decreased leaflet separation and multiple echoes filling the space between the aortic root and valve opening
- LV ejection time evaluated using the length of time the AV is open
- The presence of early systolic closure of the aortic valve indicates the stenosis is subvalvular (not valvular)
- LVH noted on LV m-mode due to pressure overload
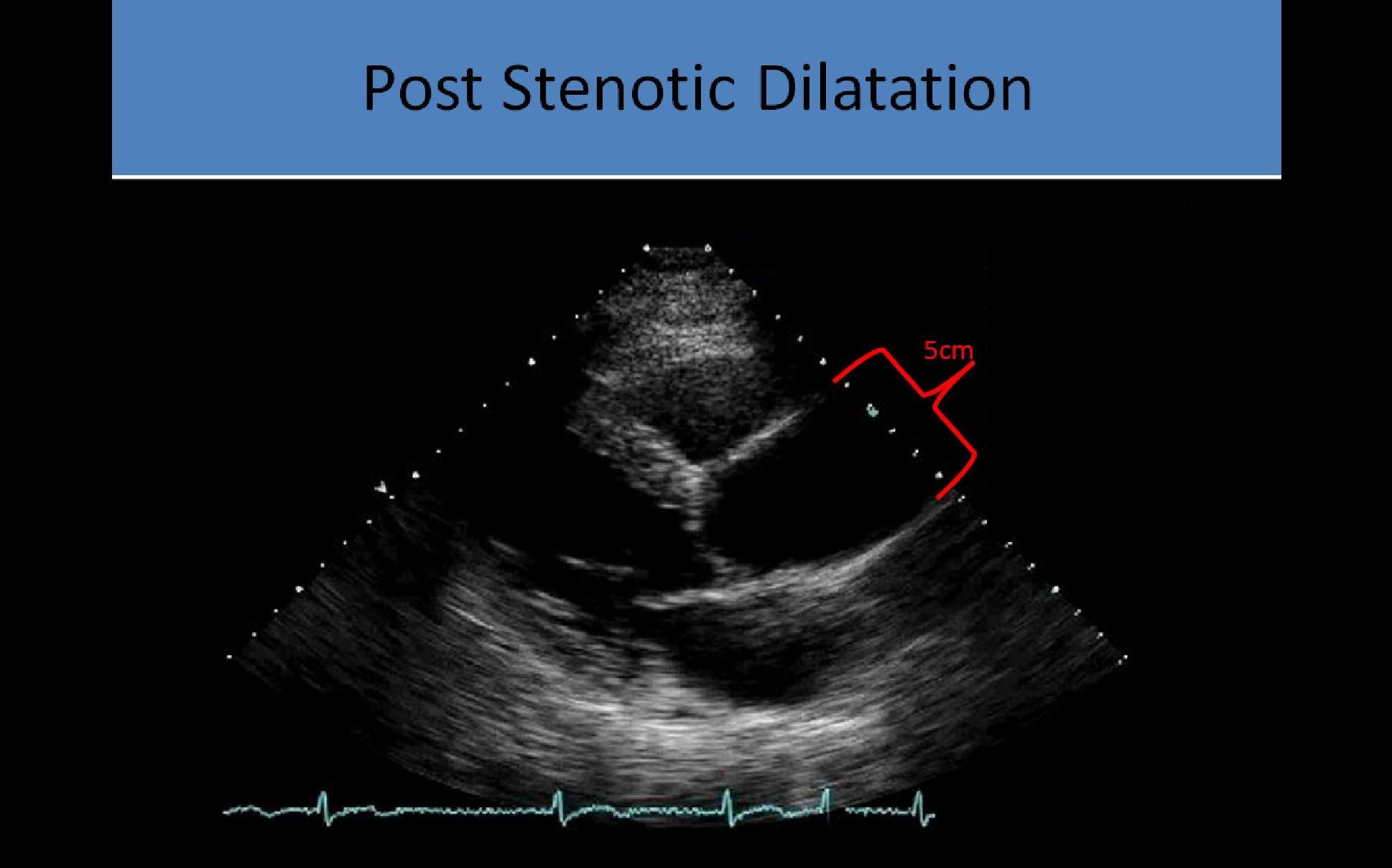
- Post stenotic aortic root dilatation due to eccentric flow through stenosis
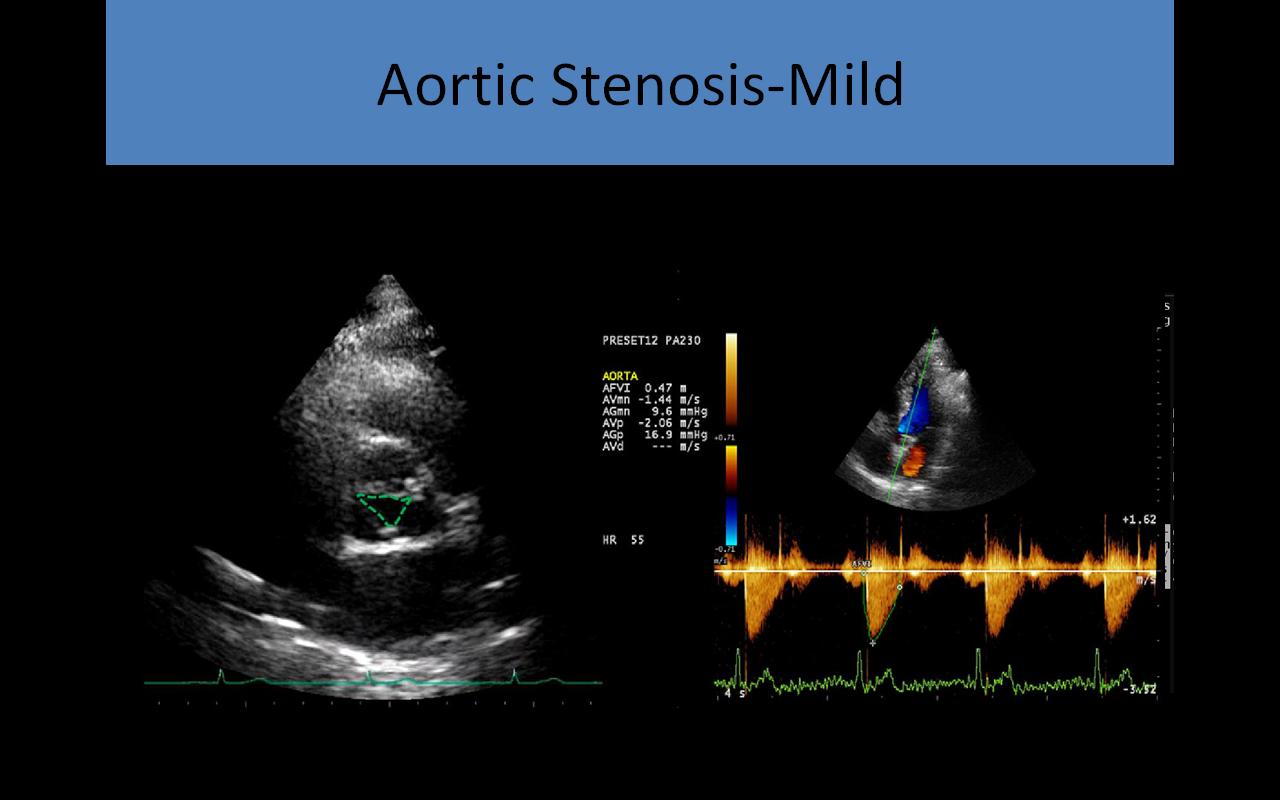
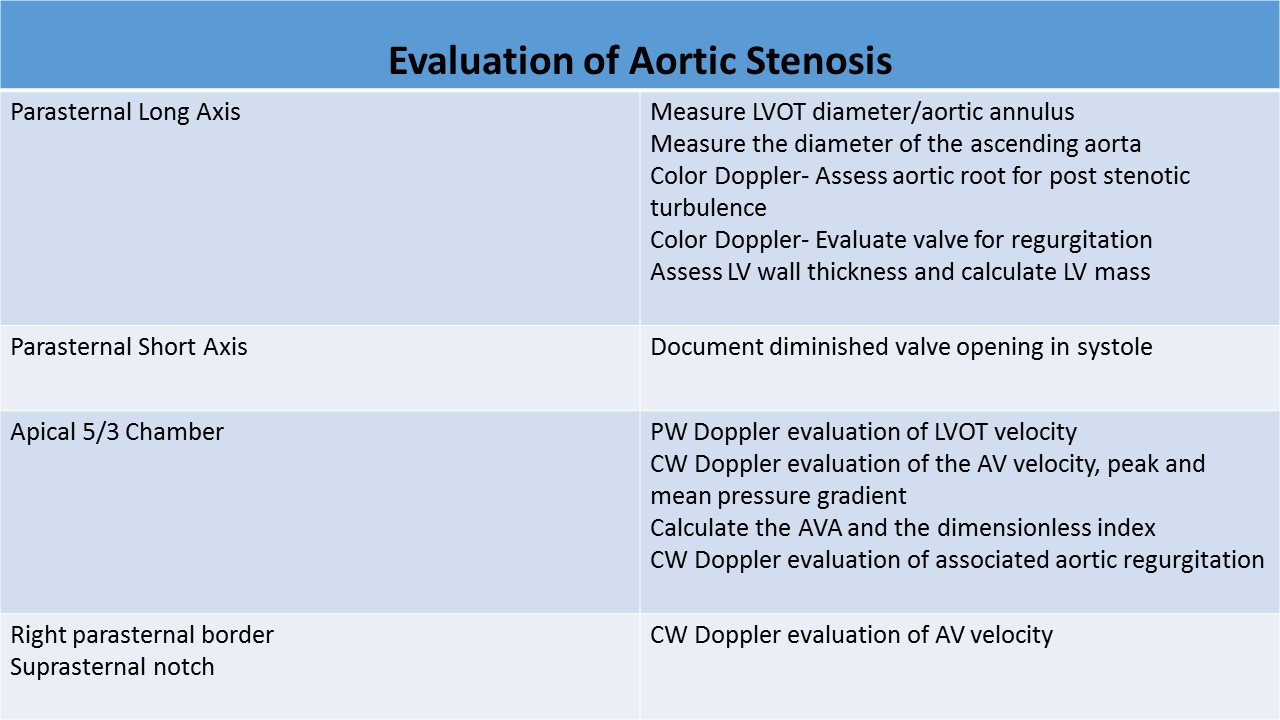
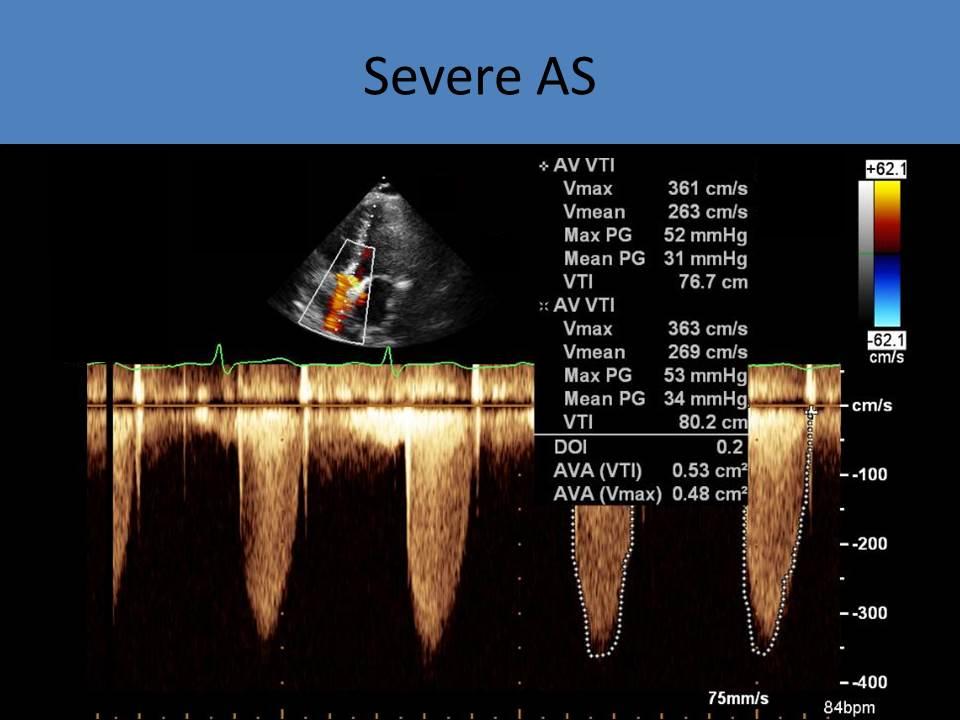
2D and Doppler Evaluation:
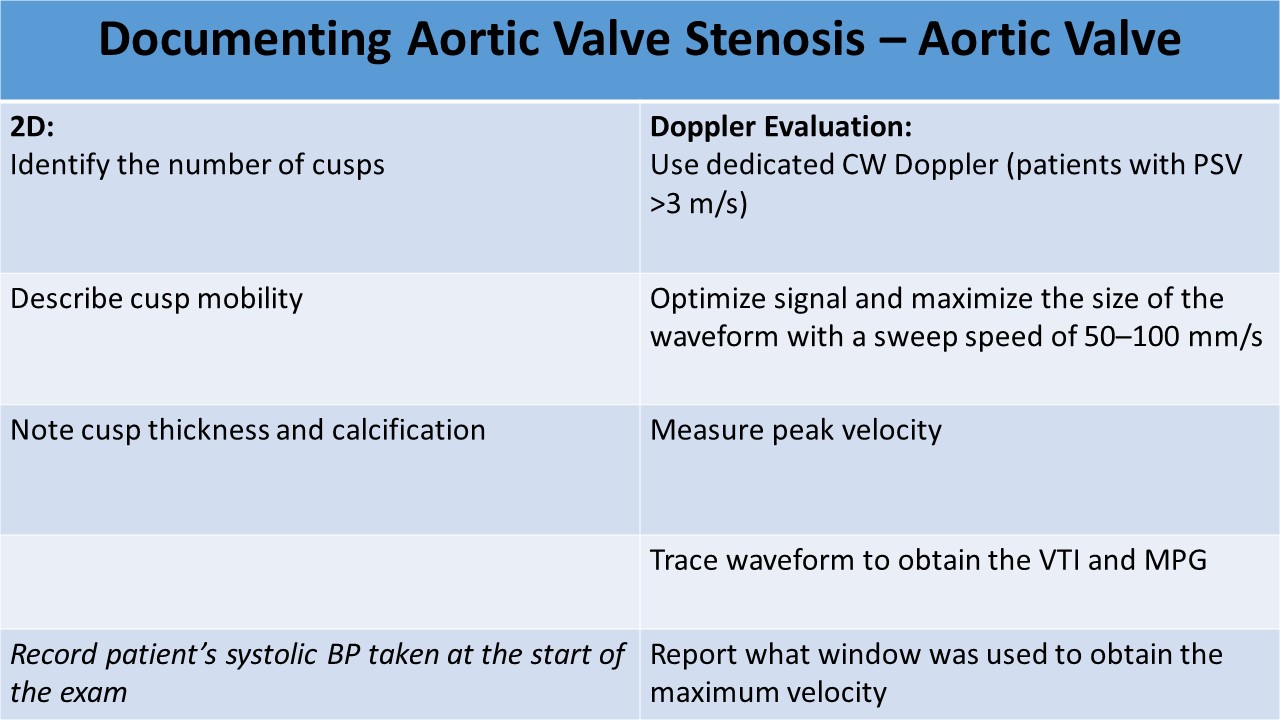
- 2D evaluation: short and long axis images used to identify the number of cusps, describe cusp mobility, thickness, and calcification
- Doppler: used to identify the location of the stenosis – subvalvular, valvular or supravalvular
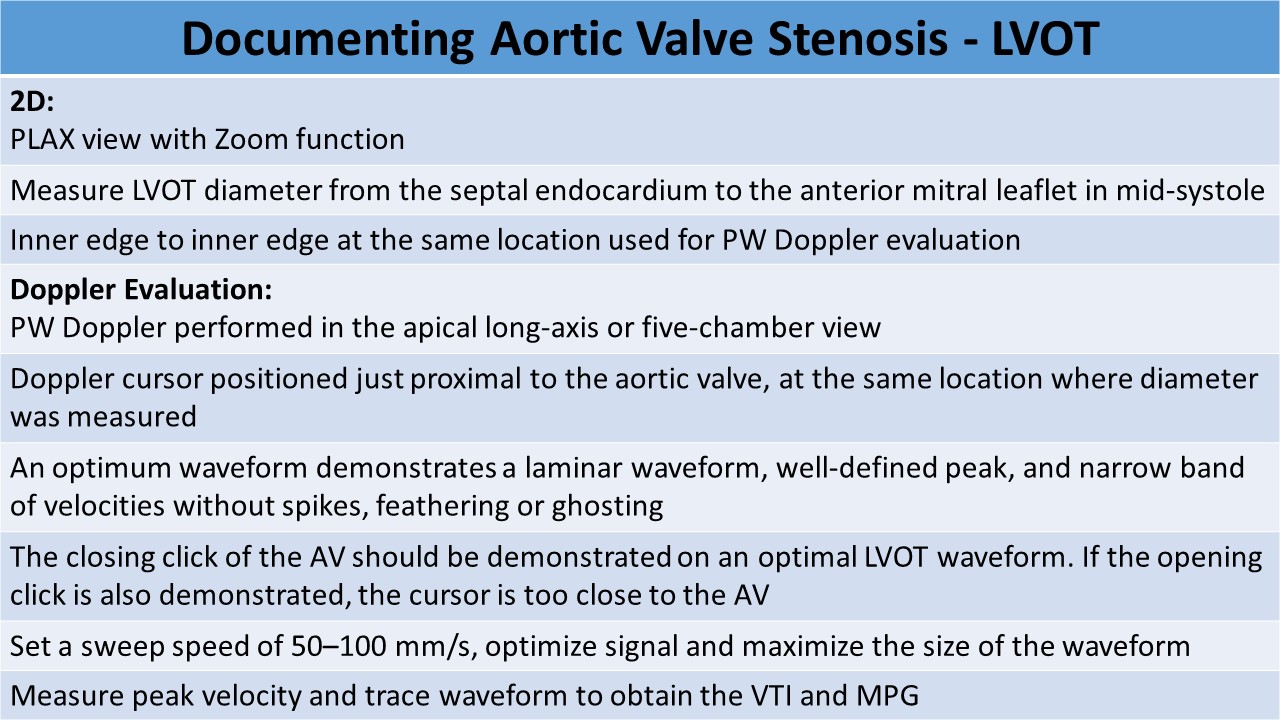
- PLAX
- Delineates the restricted opening of the tips of the aortic leaflets and systolic doming
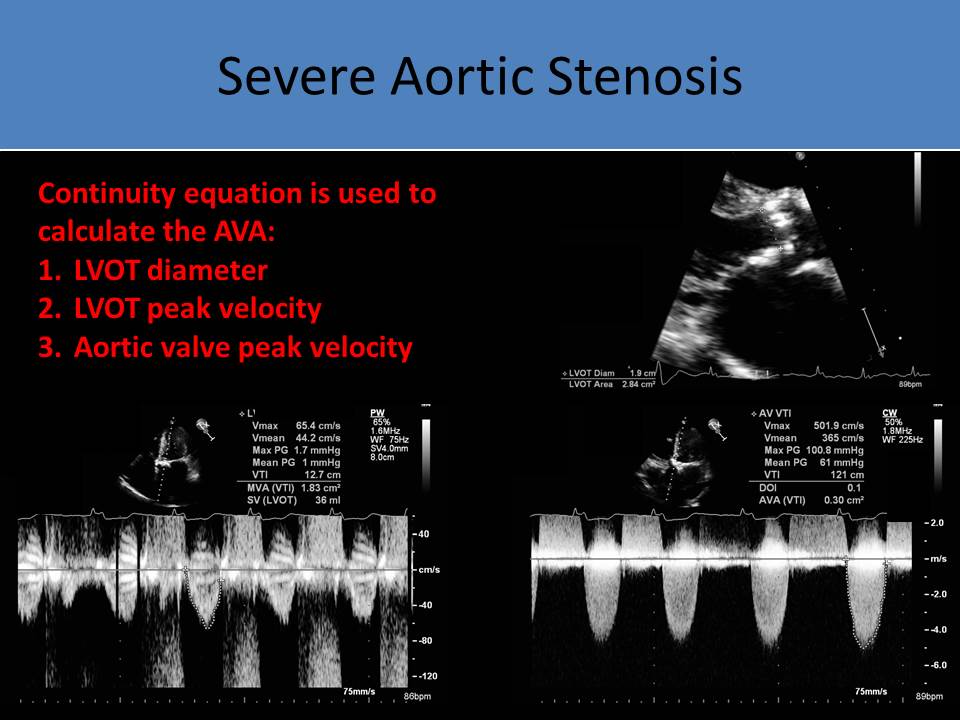
- LVOT diameter measurement performed at mid systole, inner to inner dimension
- PSAX - at the level of the aortic valve
- Demonstrates the true orifice of the stenotic valve
- Area can be traced, ****planimetry is not very accurate because heavily calcified leaflets cause bright echoes with poorly defined borders making measurement difficult
- AP 5/AP 3
- Align the Doppler cursor parallel (0 degree angle) to the flow through the LVOT/AV; more than a 20 degree incident angle can cause a significant change in calculated flow velocity
- LVOT
- PW Doppler evaluation of the performed at same location as LVOT diameter measured
- 2-3mm sample volume
- Should produce a waveform with a spectral window
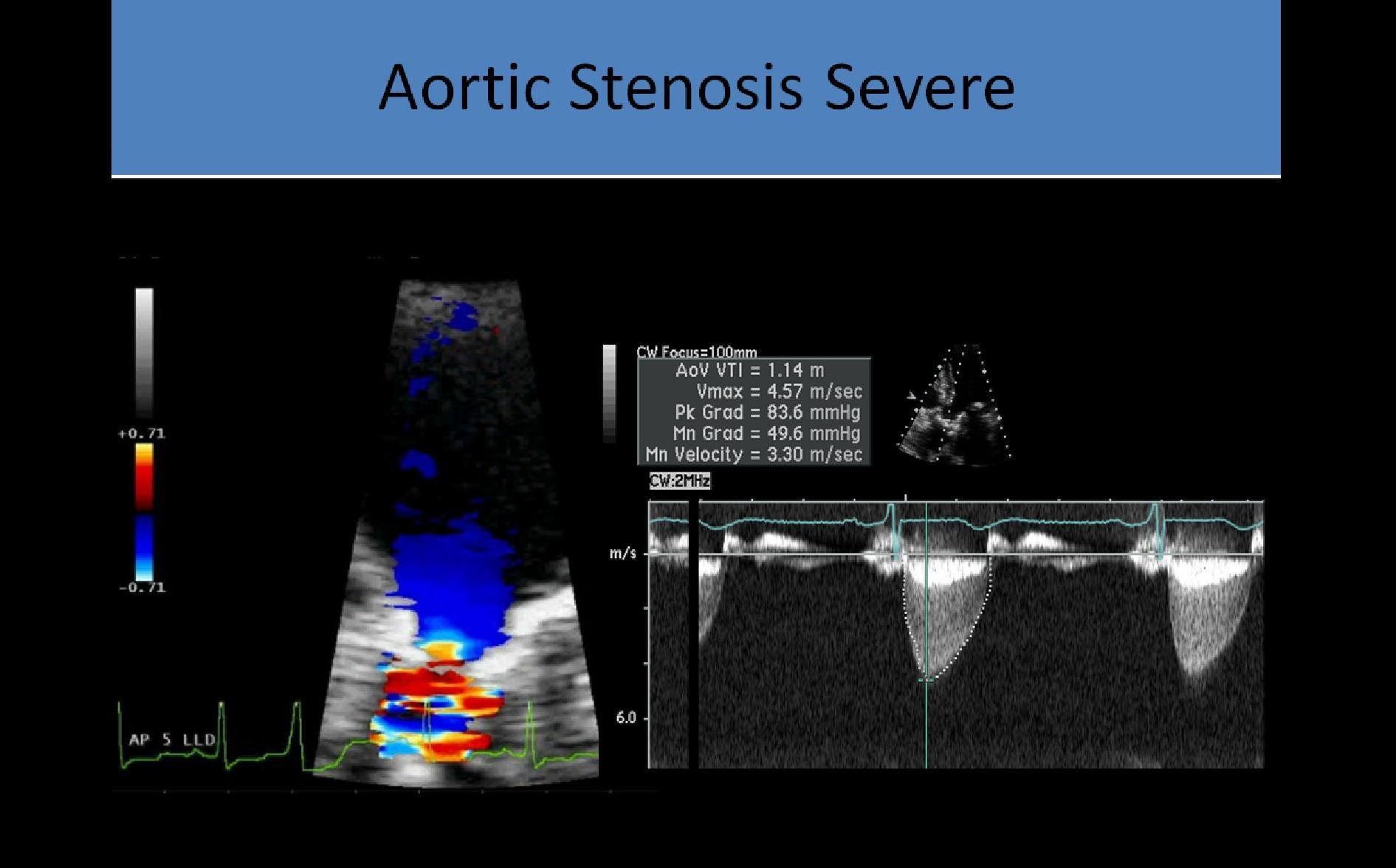
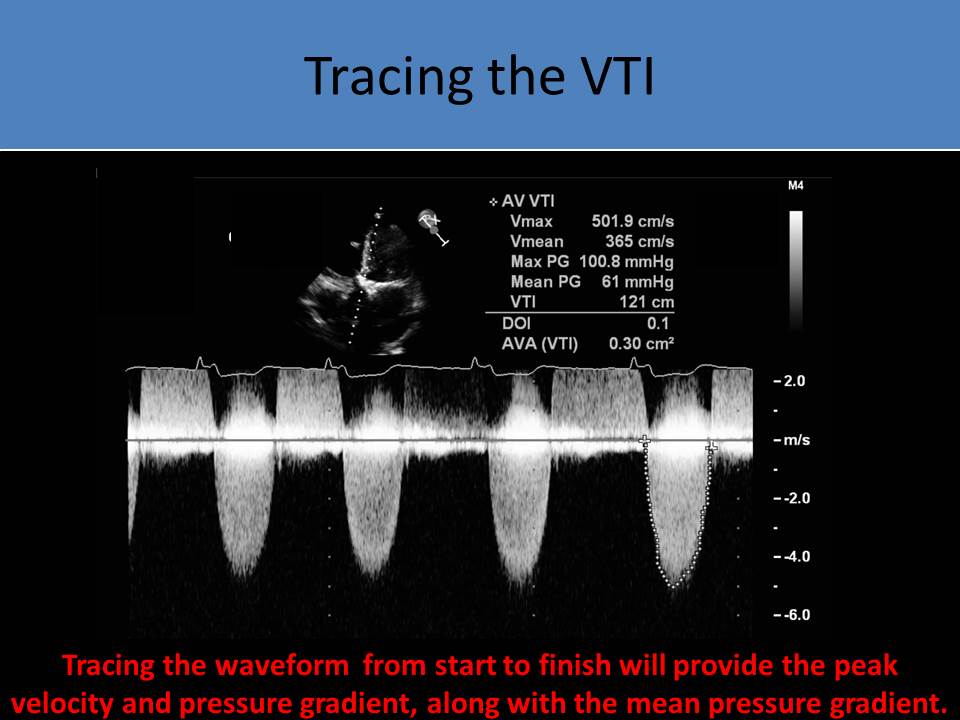
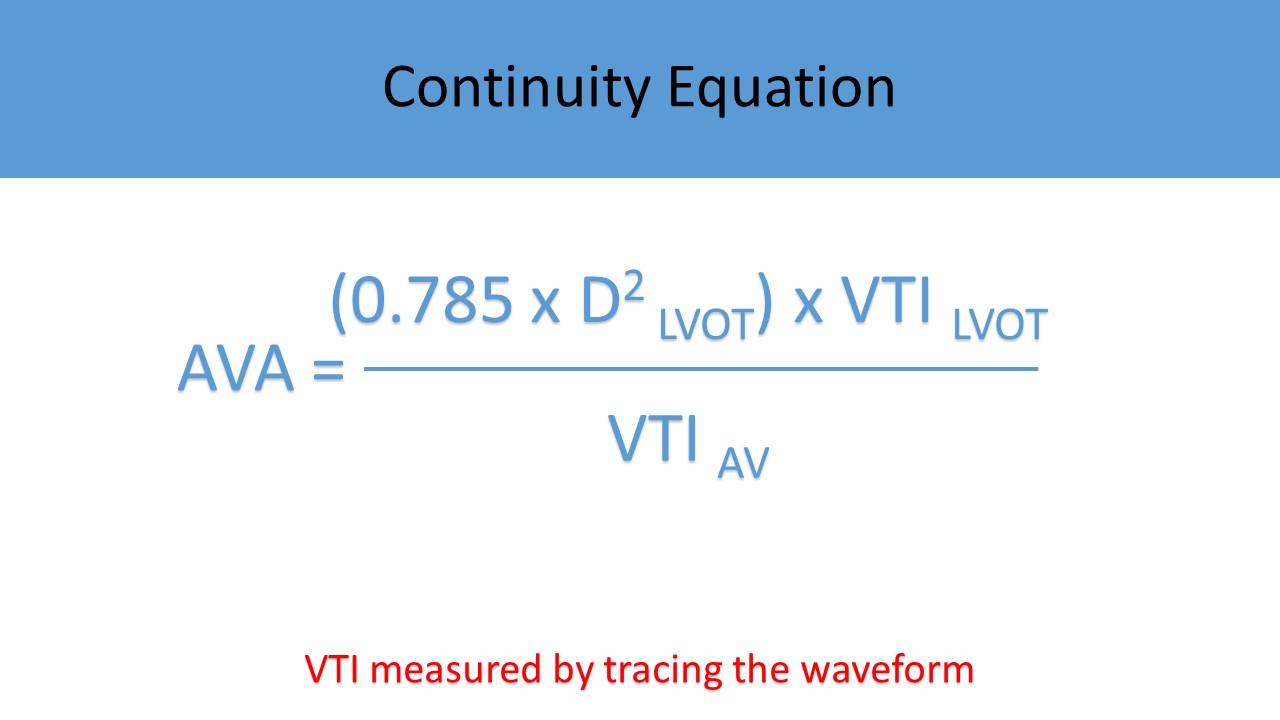
- Increase sweep speed to perform velocity time integral (VTI) measurement by tracing the outer edge of the waveform
- The peak pressure gradient (PPG) and mean pressure gradient (MPG) are also provided from the tracing
- Aortic Valve
- CW Doppler used due to high velocity and sampling depth
- NO spectral window displayed
- Increase wall filter and decrease Doppler gain
- Increase sweep speed to 100mm/s to perform VTI measurement, PPG and MPG by tracing the outer edge of the waveform
- Differences in cardiac output will cause variations in the velocity and the pressure gradient across a stenotic aortic valve
- The continuity equation corrects for differences in left ventricular function, stroke volume and cardiac output
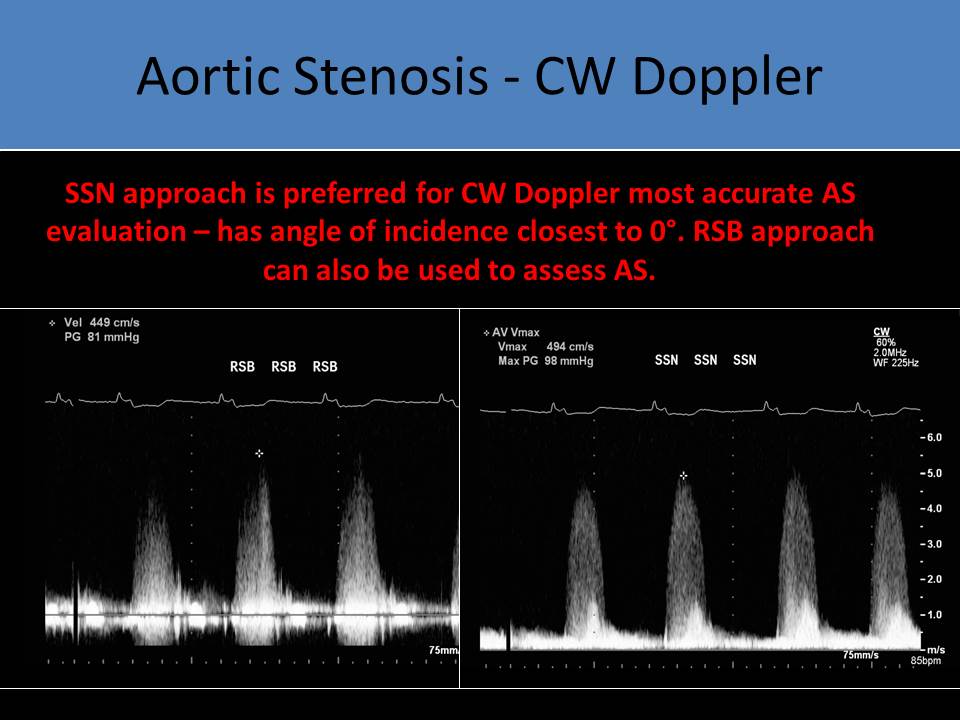
- Pedoff probe applied at the apical, right parasternal and suprasternal windows
- Different views used with an assumed 0 degree angle of insonation
- The acoustic window used for the peak velocity and pressure measurements should be recorded so the method remains constant on sequential studies
- The aortic peak systolic velocity should always be recorded from the same acoustic window as the previous exams
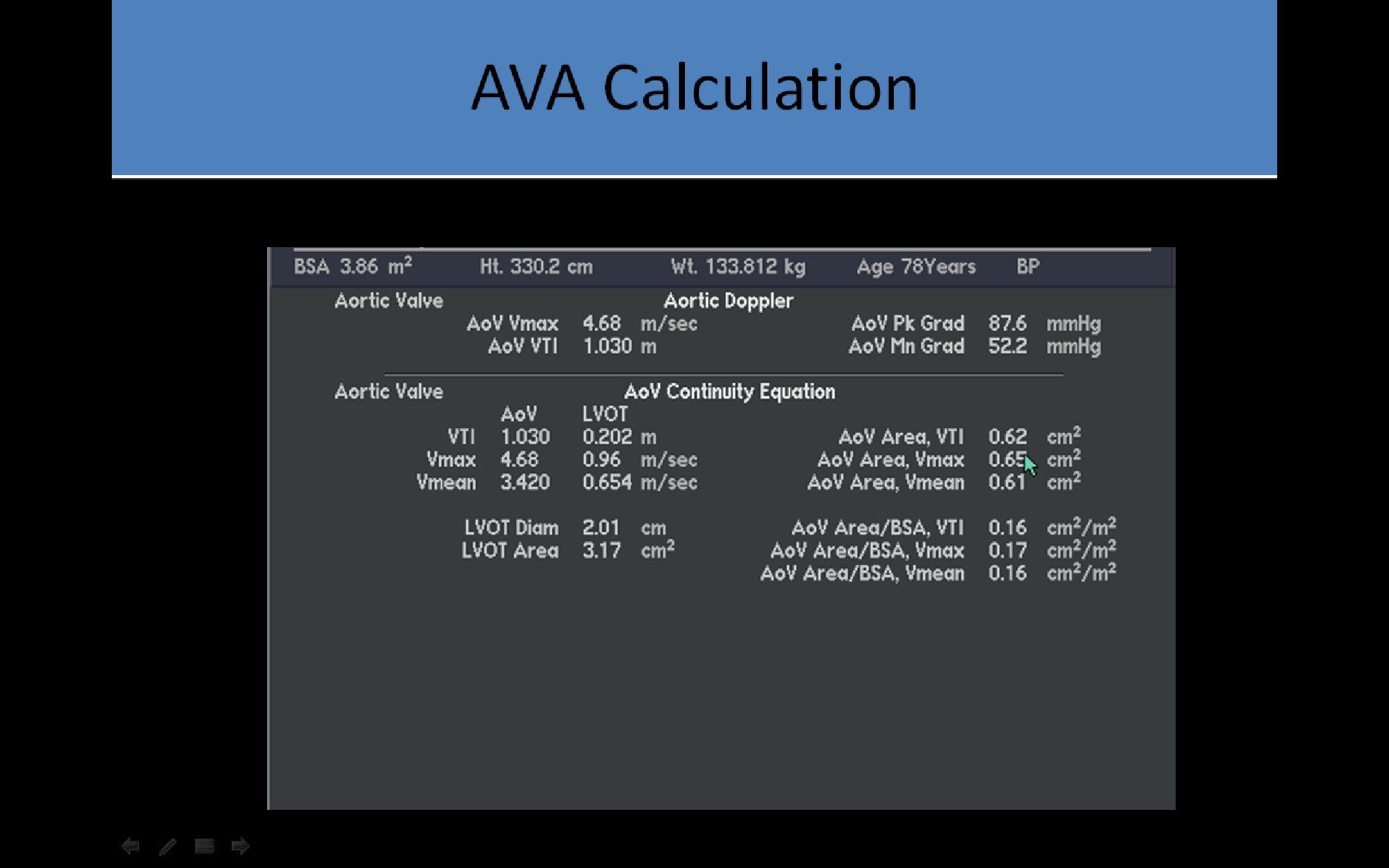
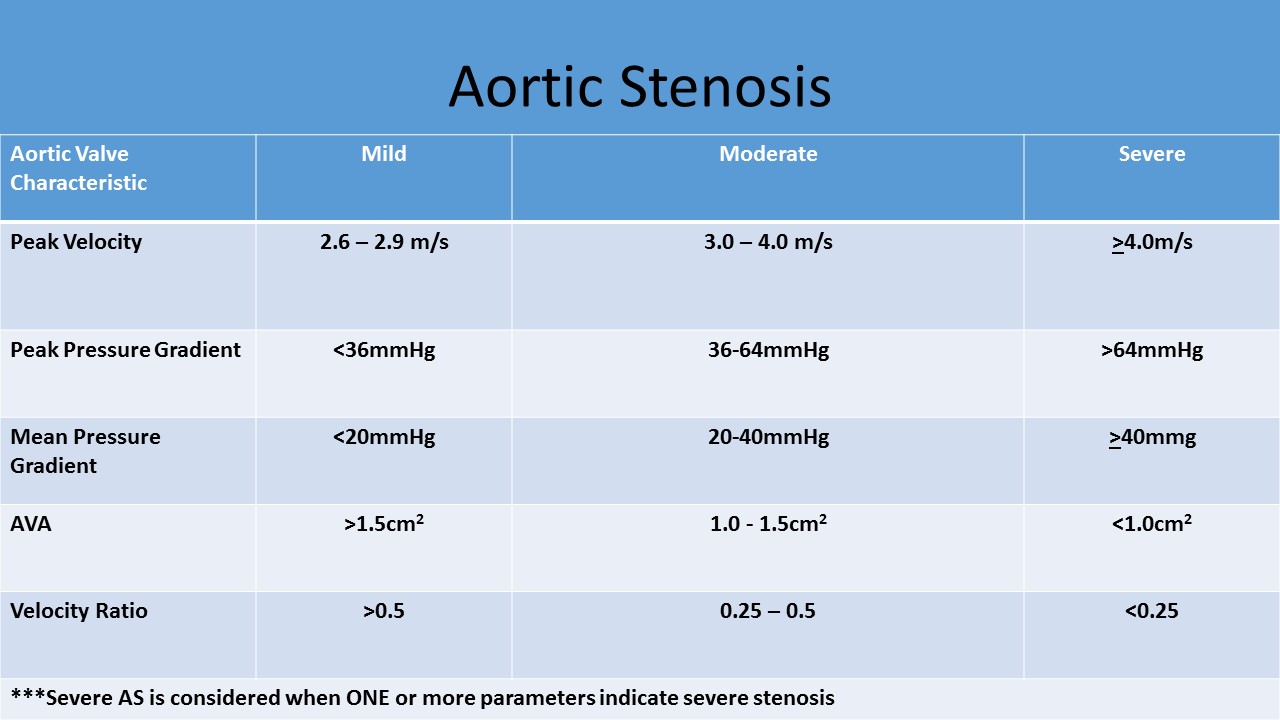
- Average normal aortic valve area is 3 - 4cm²
- Increasing velocities and pressure gradients are noted with increasing severity of stenosis
- Velocity and PPG alone cannot diagnose stenosis due to variations in cardiac output, you must know the valve area
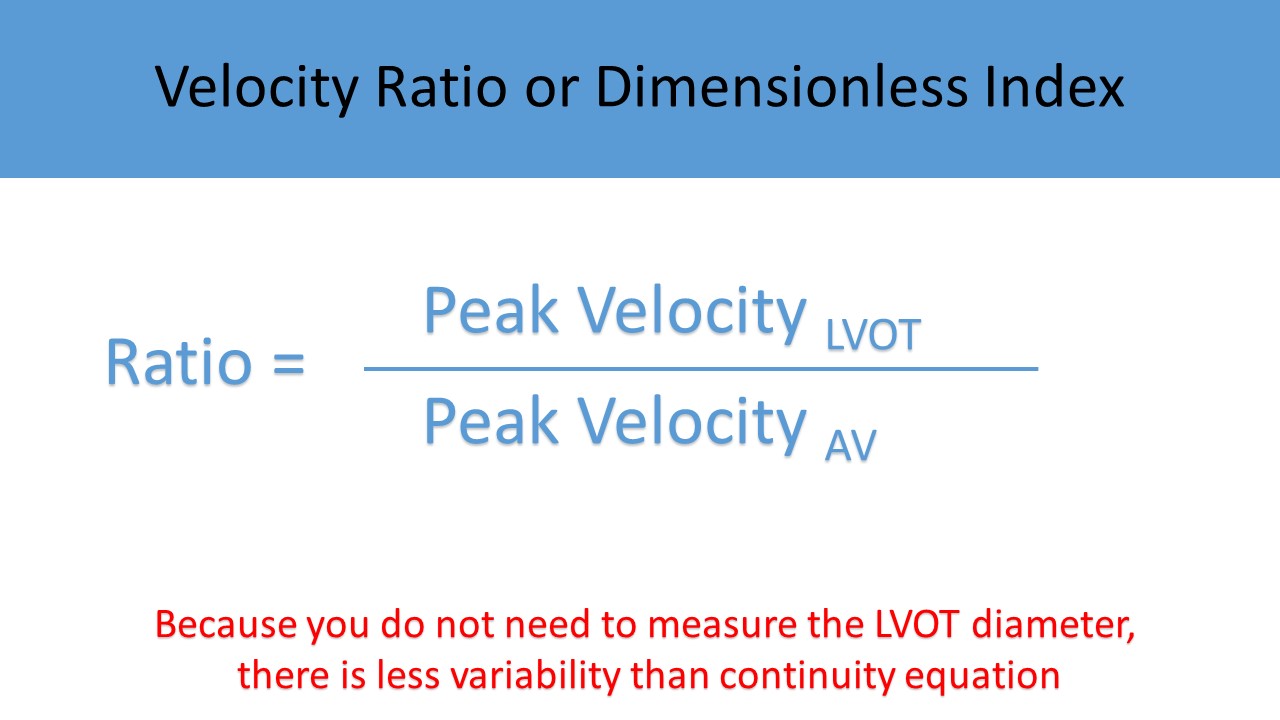
- Velocity Ratio and VTI Ratio are methods used to reduce errors in AVA calculation due to inaccurate measurement of the LVOT diameter
- Severe regurgitation can falsely elevate the peak velocity and pressure gradients but the AVA and velocity ratios should still be accurate
- PPG is not an accurate method of assessing aortic stenosis in patients with severe aortic insufficiency; left ventricle becomes hypercontractile due to the continuous reprocessing of the same blood; PPG will be higher than the actual gradient related to the stenotic valve
- MPG can be used to assess valvular gradient in aortic stenosis patients who also have significant aortic insufficiency
- MPG calculated on Doppler best correlates with the mean pressure gradient obtained during heart catheterization
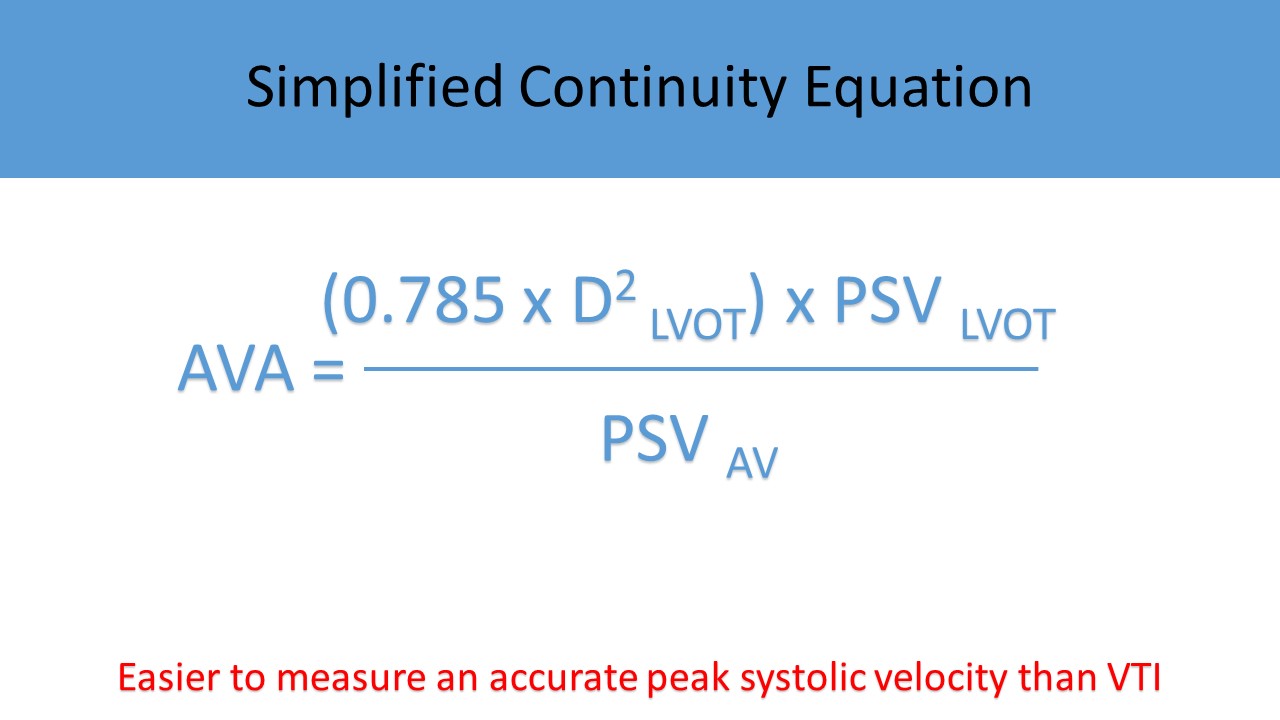
- Continuity Equation
- Used to calculate the AVA
- Corrects for differences in left ventricular function, stroke volume and cardiac output on serial exams
- Requires careful 2D measurement of LVOT diameter and accurate cursor placement for recording of velocity measurements
- Numerous factors can cause incorrect calculation of the AVA
- Cannot be used to assess a transcatheter aortic valve replacement (relies on pressure gradients and the velocity ratio to assess stenosis)
- Incorrect LVOT Measurement:
- Because the LVOT diameter is squared for the calculation of CSA, it is the greatest potential source of measurement error in the continuity equation
- Calcification of the aortic annulus can extend to the base of the anterior mitral leaflet causing inaccurate LVOT diameter measurements A ‘sigmoid septum’ can cause the underestimation of the LVOT diameter
- If the PLAX view is poor, the diameter can be overestimated = larger AVA or the diameter can be underestimated = smaller AVA
- When the calculated AVA changes on serial exams, look for differences in the components incorporated in the equation
- LVOT size rarely changes over time in adults with stable hemodynamic conditions
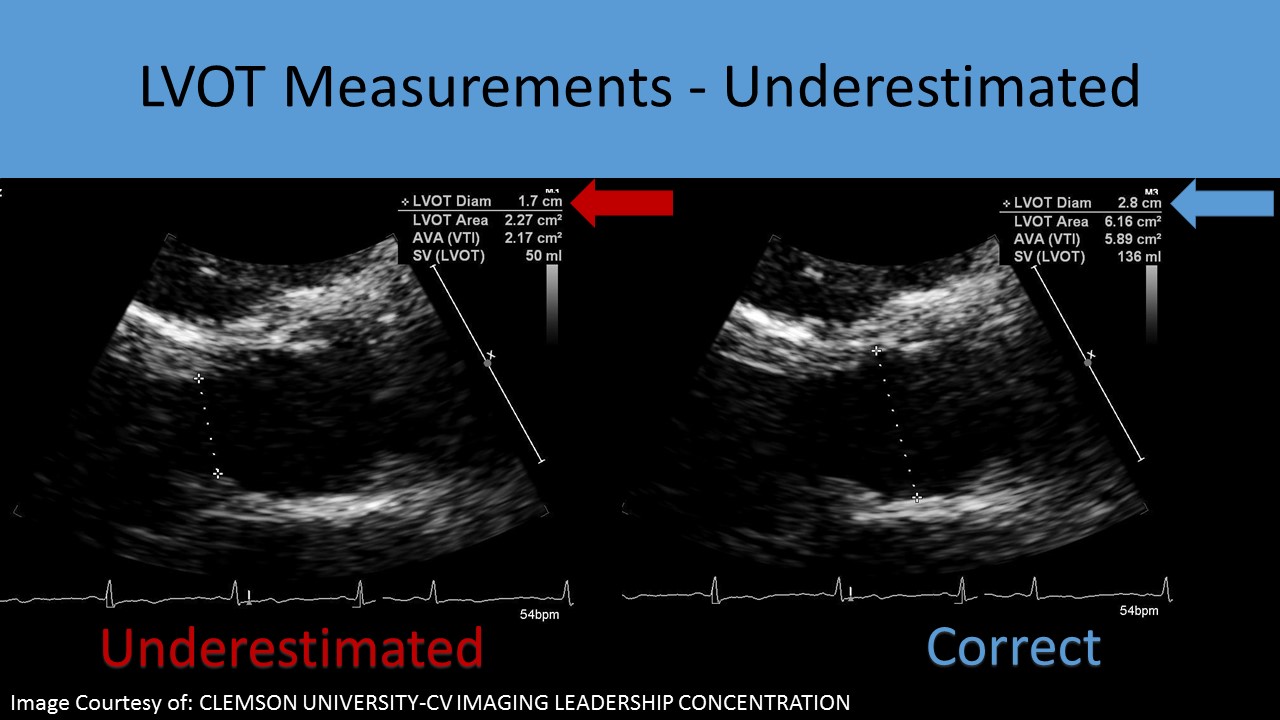
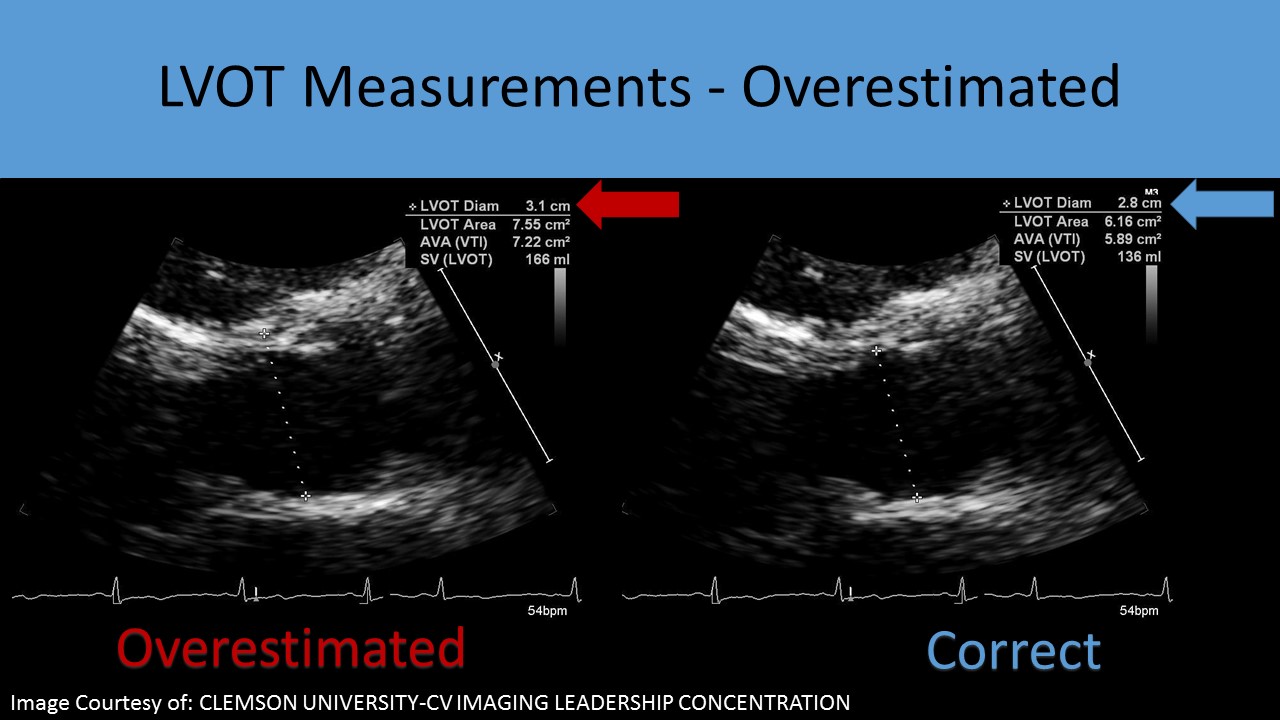
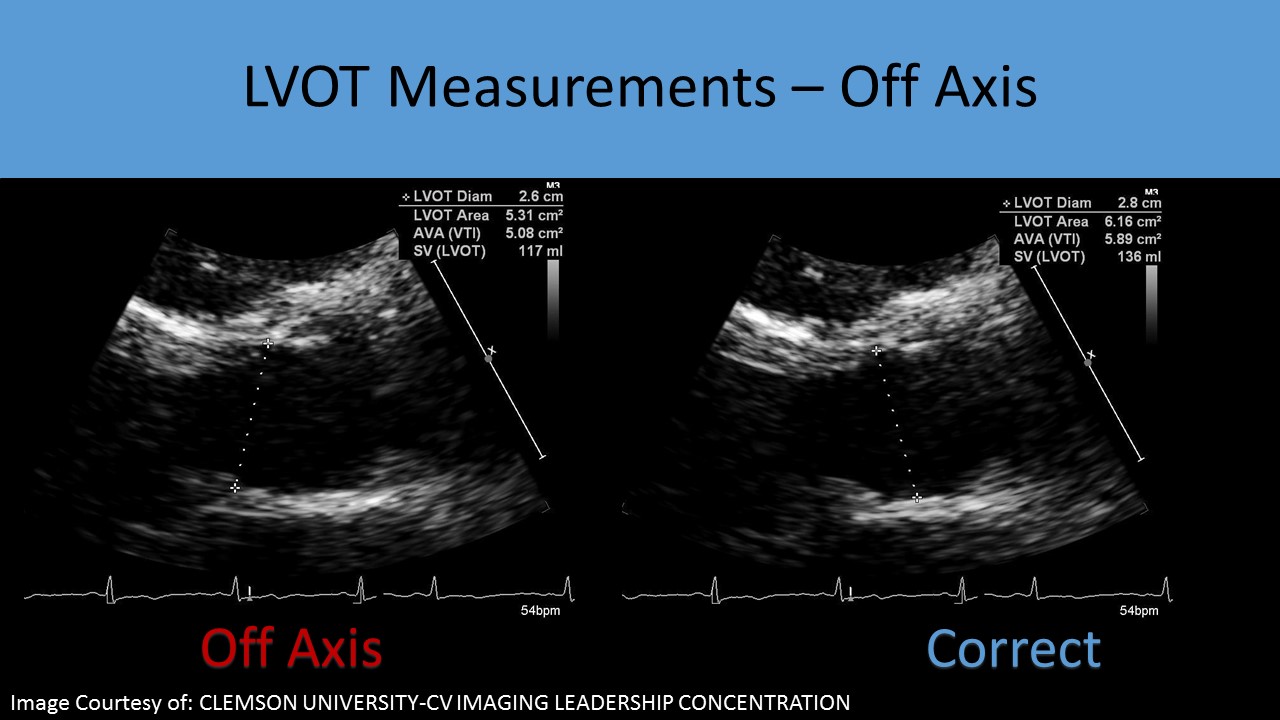
- Other causes of incorrect results for calculating aortic valve area using the continuity equation:
- Poor Doppler cursor alignment with flow through the LVOT or AV
- Doppler cursor placement too close to LVOT
- records higher velocity that is used in continuity equation
- underestimates stenosis
- overestimates AVA or larger AVA
- can explain an AVA that indicates moderate stenosis but AV velocity and peak pressure gradients indicate severe stenosis
- Doppler cursor placement too far from LVOT
- records lower velocity that is used in continuity equation
- overestimated stenosis
- underestimated or smaller AVA
- can explain an AVA that indicates severe stenosis but AV velocity and peak pressure gradients indicate moderate stenosis
- Heavy calcification on the leaflets can lead to underestimation of stenosis due to degraded Doppler signal and inability to locate the highest velocity
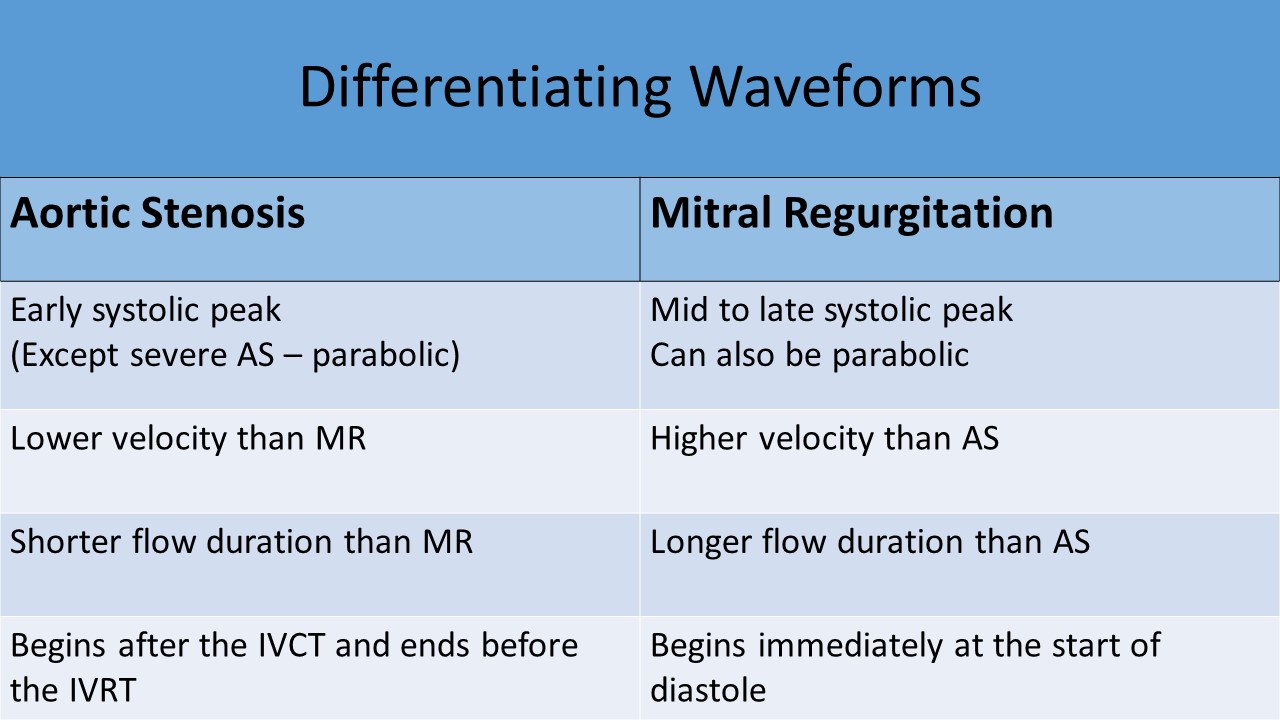
- Mistaking mitral regurgitation jet for aortic flow
- Both MR and AV velocities are demonstrated on the under side of the baseline
- MR jets are longer in duration that the AV flow
- MR jets peak later than the tracing from the AV (difference in acceleration times)
- MR peak velocity is higher than the peak velocity across the AV
- Sub-aortic or supra-aortic stenosis
- Using aortic tracing following a PVC
- The PVC will produce an early contraction with a lower velocity waveform
- The waveform after the PVC will demonstrate a higher velocity waveform that compensates for the previous premature contraction
- Atrial fibrillation
- Flow velocity should be averaged across 5or more beats in AS patients with atrial fibrillation
- When there is a long R-R interval, the PSV measurement is higher on the next beat
- When there is a short R-R interval, the PSV measurement is lower on the next beat
- Systolic BP is elevated
- Hypertension can affect the peak velocity/mean gradient across the valve
- Systolic BP should be recorded on each exam
- The optimal evaluation of aortic stenosis should be performed when the patient’s blood pressure is normal

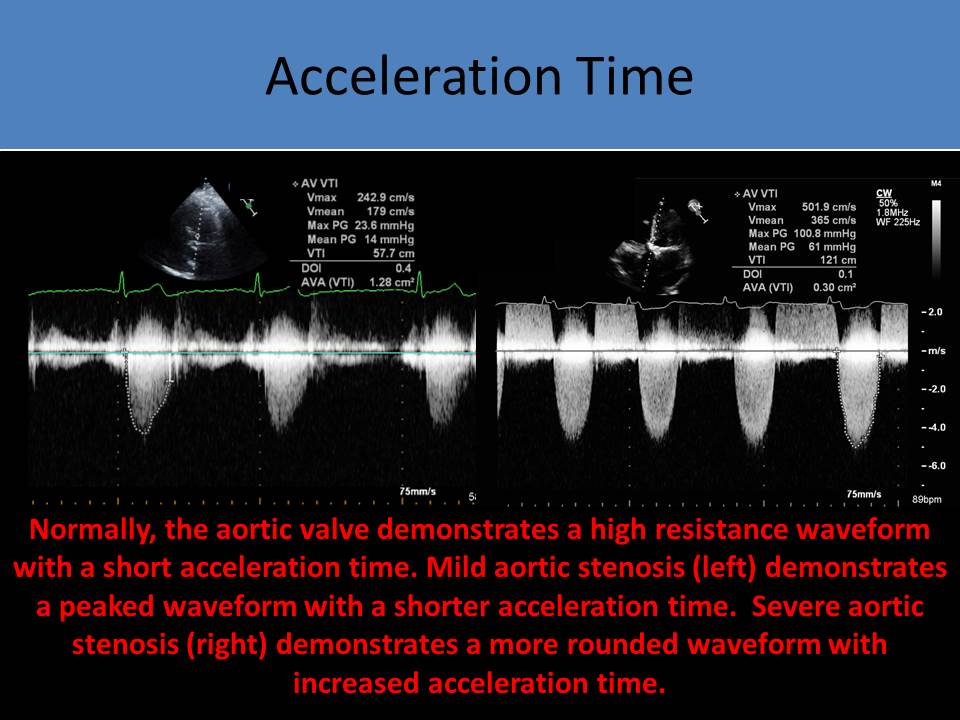

Secondary Findings:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy with left heart pressure overload
- Increased LV mass
- Dilated aortic root
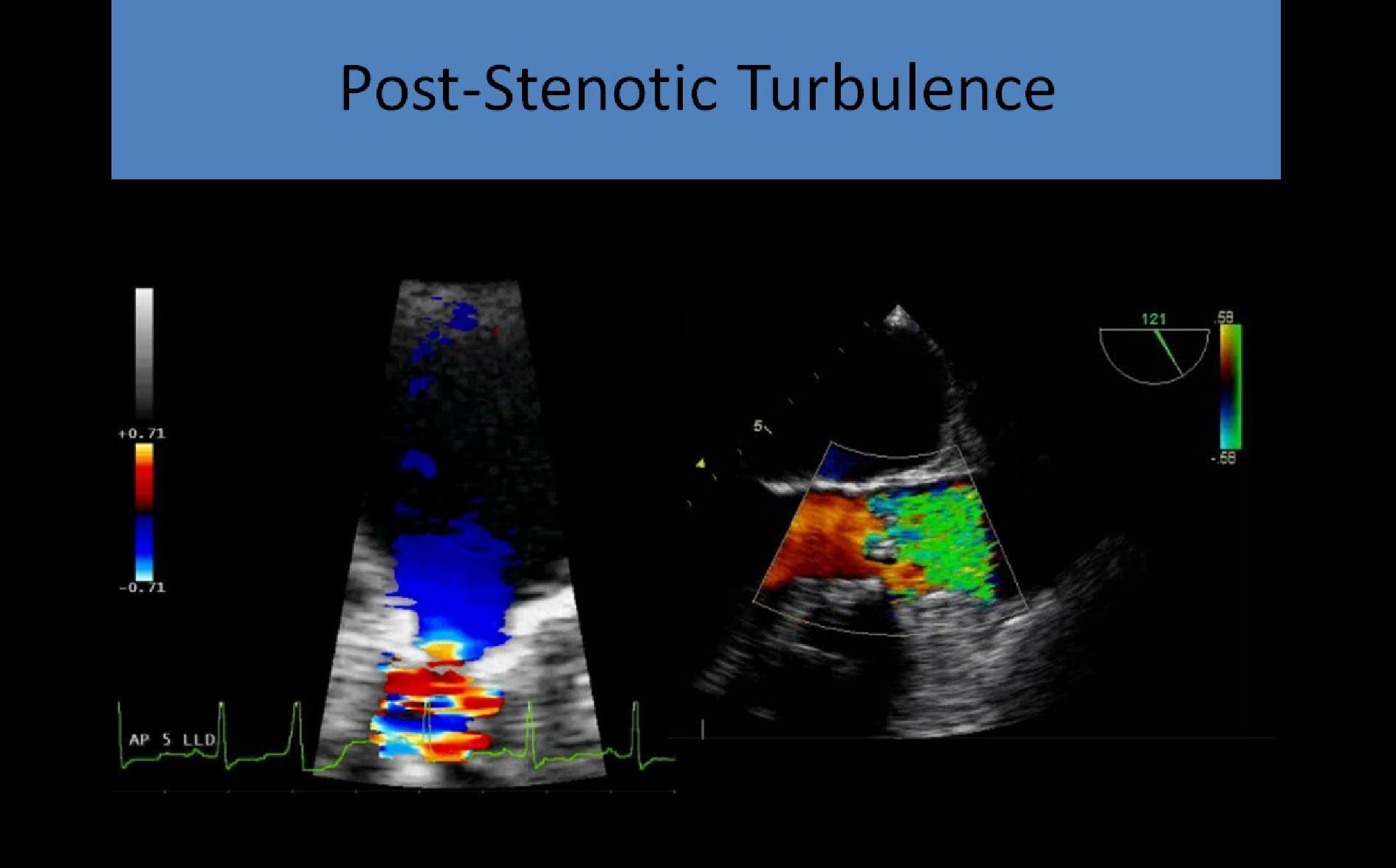
- Turbulence distal to the valve
- Can be associated with CVA/Stroke due to decreased flow to brain and embolus potential from atherosclerotic disease on cusps
- Aortic regurgitation – most patients have mild to moderate regurgitation
- Mitral regurgitation - MR severity does not affect evaluation of AS severity
- Mitral stenosis - can result in low cardiac output and low flow volume, low gradient AS
- Dilated aortic root
- Systemic HTN